Particle Types¶
The particle type defines how particles move through space (e.g. velocity, acceleration) and how they look (e.g. size, color). Each particle emitter has a list of assigned particle types, which it will use for generating particles.
In the object browser, particle types are shown below the list of nodes. You can assign a particle type to a particle emitter by dragging and dropping it on the particle emitter in the node list:
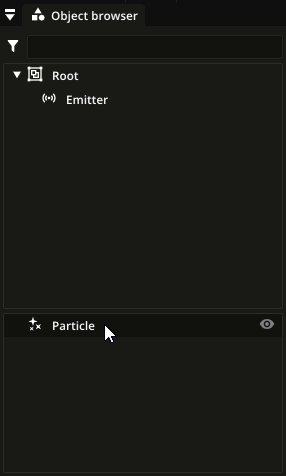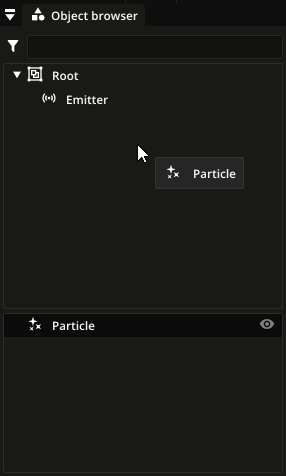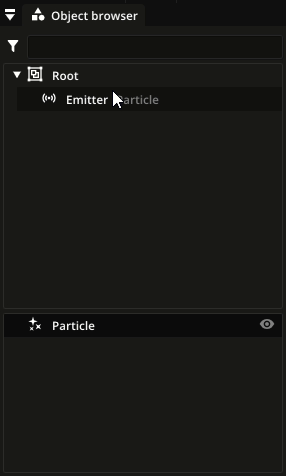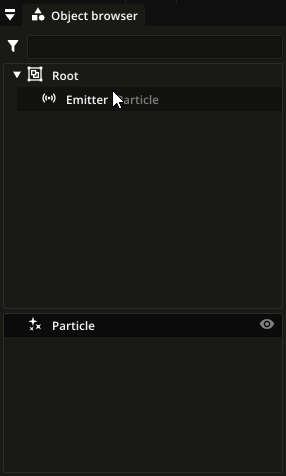
Particle sub-types¶
To create complex effects it is often necessary for particles to be spawned after one another, for example a smoke particle created from a fire particle. In the object browser, drag & drop a particle type onto another particle type to make it a sub-type of the latter. This way, particles of the sub-type are generated at the positions of particles of the parent particle type. Note that the Primary property of sub-type’s emitter needs to be disabled.
Particle renderers¶
There are three distinct types of particles, which determines how they are rendered.
- Sprite particle
The sprite renderer renders each particle as a separate sprite.
- Trail particle
The trail renderer generates continuous trails along the path of particles with the same parent particle. You can set details of the trail mesh generation in the additional settings next to the renderer property.
- Mesh particle
The mesh renderer renders each particles as a three-dimensional mesh. You can change which mesh is used in the additional settings next to the renderer property.
Properties¶
The following properties can be adjusted in the property window to influence the look and behavior of the particles.
General¶
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Lifespan |
How long particles exist after being spawned by their emitter. |
Lifespan variance |
How much the lifespan varies between particles. |
Number |
How many particles of this type are spawned by the emitter. |
Position |
Motion path of particles, shown in the scene view if the property is selected. If Attached to Emitter is selected, the position of particles is tied directly to the position of their emitter. |
Motion path force |
How much particles are influenced by the motion path. Set to 0 to disable motion paths. |
Visual¶
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Material |
Material that particles use for rendering. The parameters of the active material can be accessed with . See particle materials for details. |
Renderer |
Renderer used to generate the particle geometry. Click to show additional options for each renderer. |
Layer |
Layer on which particles are drawn. Particles on upper layers occlude those on lower layers. |
Color |
Color of particles over their lifetime. Double-click or right-click the color gradient to add another color. Double-clicking a color marker lets you choose its color, right-clicking removes it. To change the position of color markers, drag them around using the mouse. |
Color variance |
How much the color varies between particles. |
Initial opacity |
Opacity of each particle when created. |
Opacity |
Opacity of each particle over its lifetime as a fraction of its initial opacity. |
Opacity variance |
How much the opacity varies between particles. |
Initial size |
Size of each particle when created. |
Size |
Size of each particle over its lifetime as a fraction of its initial size. |
Size variance |
How much the size varies between particles. |
Stretch |
How much particles are stretched based on their speed. |
Motion¶
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Initial velocity |
How fast each particle is initially after being spawned by the emitter. |
Inherited velocity |
How much speed particles inherit from the parent particle or emitter. |
Velocity variance |
How much the speed varies between particles. |
Acceleration |
Linear acceleration applied to each particle over its lifetime. Positive values speed up particles, while negative values slow them down. |
Radial acceleration |
Acceleration of each particle towards the emitter over its lifetime. If you select negative values here, particles are repelled from the emitter. |
Alignment mode |
|
Rotation mode |
Whether the rotation property represents the exact rotation of particles or their angular velocity. |
Initial rotation |
Rotation of each particle when created, in degrees. For 3D effects, rotation is composed of roll, yaw and pitch. |
Rotation |
How particles rotate over time from their initial rotation. |
Rotation variance |
How much the rotation varies between particles. |
Angular velocity variance |
How much the angular velocity varies between particles. |
Rotation by speed |
How much particles rotate based on their velocity. |
Pivot |
Center of rotation, relative to the particle’s center. |
Physics¶
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Physical size |
The relative size of particles for motion and collision calculations. |
Weight |
How strongly particles are affected by force fields. |
Bounce |
How strongly particles bounce off colliders after collisions. |
Friction |
How resistant particles are to sliding down colliders. |